SpaceX’s Starship Booster Catch Demonstrates A Giant Leap in Reusable Rocket Technology
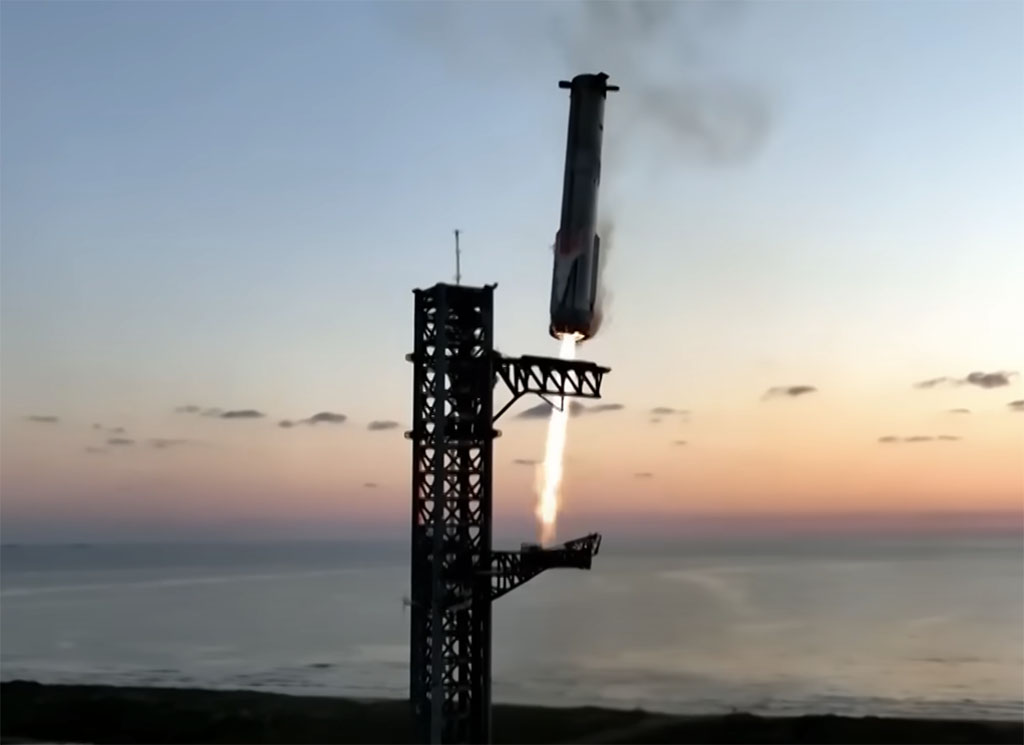
On Sunday, SpaceX achieved a new milestone in space travel by successfully catching the Starship rocket booster mid-air using mechanical arms at the launch pad. This achievement is a major step in reusable rocket technology, bringing Elon Musk’s vision of interplanetary travel closer to reality.
Starship’s Bold Test Flight
At sunrise, the towering 400-foot Starship lifted off from southern Texas. Unlike previous launches, this fifth test did not end in a fiery explosion. Instead, it marked a significant breakthrough in booster recovery technology.
IS YOUR COMPUTER SECURE?
FREE Malware Removal
Detect & Remove Adware, Viruses, Ransomware & Other Malware Threats with SpyHunter (FREE Trial)
IS YOUR COMPUTER SECURE?
FREE Malware Removal
Detect & Remove Adware, Viruses, Ransomware & Other Malware Threats with SpyHunter (FREE Trial)
IS YOUR COMPUTER SECURE?
FREE Malware Removal
Detect & Remove Adware, Viruses, Ransomware & Other Malware Threats with SpyHunter (FREE Trial)
Musk, excited by the accomplishment, called it “science fiction without the fiction part.” The most remarkable part? The booster didn’t just return to Earth safely—it was caught mid-descent by SpaceX’s custom-built mechanical arms, known as “chopsticks.”
The Importance of the Catch
SpaceX has been refining its rocket recovery process for nearly a decade. The Falcon 9, which has successfully landed on platforms, has already saved the company millions. However, catching a booster directly at the launch pad raises the bar for reusable rockets.
This evolution in recovery could eventually make rocket launches even more efficient and cost-effective. Musk aims to apply this technology to Starship—the largest, most powerful rocket ever built, with 33 methane-fueled engines on its first stage.
Pushing Space Boundaries
The landing and catch weren’t the only highlights of Sunday’s flight. After separating from the booster, the Starship spacecraft orbited the planet before landing in the Indian Ocean. This successful flight added to SpaceX’s record of pushing the boundaries of space exploration.
The Starship booster, despite the intense heat and forces of the descent, showed minimal damage—mostly some warping on its outer engines, which Musk said could be easily repaired.
NASA is closely watching SpaceX’s progress. The agency has already commissioned Starship for future lunar missions under its Artemis program. With reusable rocket technology, SpaceX could send humans not just to the moon but eventually to Mars.
Sunday’s successful catch is a major milestone on the journey toward this goal. It represents the future of space travel, where rockets are fully reusable and space missions are more accessible and sustainable.
The Road Ahead
While the achievement marks a significant leap, there’s still more testing to be done. Each flight brings new data, guiding improvements for future missions. SpaceX continues to enhance the design, software, and performance of Starship with each iteration.
Musk’s goal is ambitious: to make space travel affordable and sustainable. By successfully catching the Starship booster at the launch pad, SpaceX has taken one giant leap toward making space accessible on a much larger scale.